FCA Incoterm:Application Guide in Shipping
27 Sep, 2024
Introduction
FCA (Free Carrier) is an important term in the incoterms formulated by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), and YQN Logistics will discuss in depth the working principle of FCA, the cost responsibility, and compare it with FOB (Free On Board) in this article. YQN Logistics also welcomes your further inquiries.
Definition of FCA
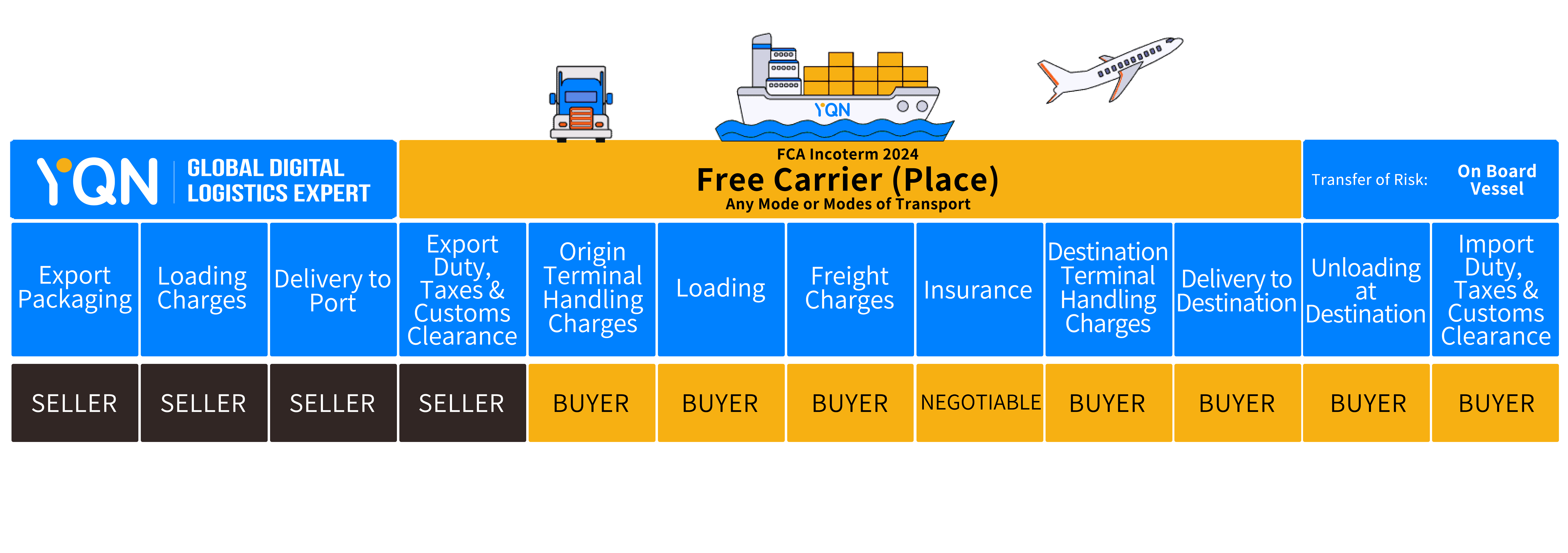
FCA allows the seller to deliver the goods to a carrier designated by the buyer, a process that usually takes place at a named location in the seller's country.
Under FCA Incoterms, the seller bears the cost and risk of transporting the goods to the named location, and the risk is transferred to the buyer once the goods are handed over to the carrier. This arrangement simplifies the international transportation process and provides flexibility for both parties.
How FCA works
There is a clear distinction between the responsibilities of the seller and the buyer under FCA regarding who pays for the transportation and the allocation of responsibility:
Seller's Responsibility: Under the terms of the FCA, the seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the named carrier and bears all associated costs and risks. This includes export customs clearance, transportation costs, and safe delivery of the goods to the carrier.
Buyer's Responsibility: The buyer is responsible for all costs and risks after the goods are delivered to the carrier, including international transportation and import customs clearance.
FCA vs FOB
There are several key differences between FCA and FOB:
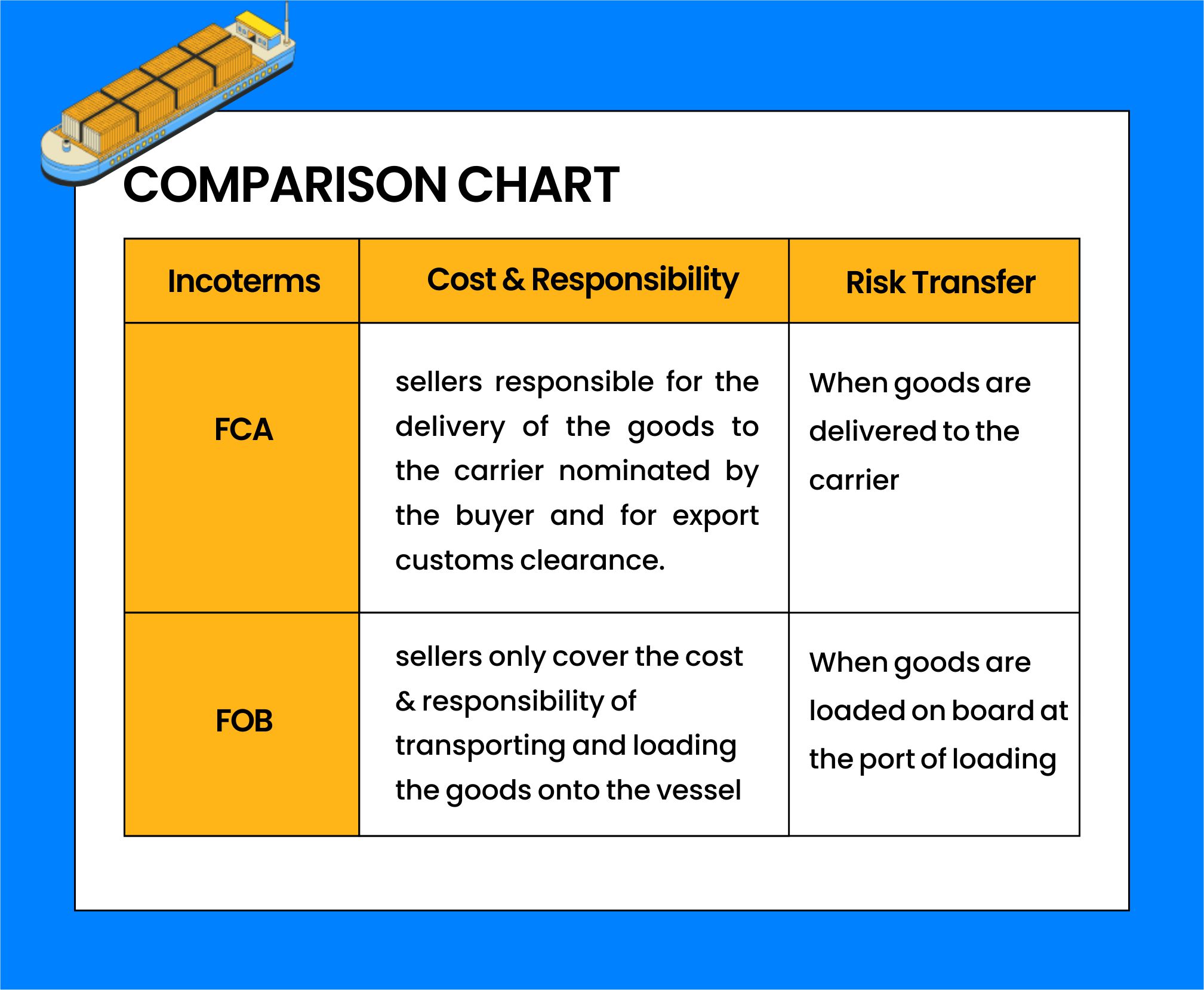
Place of Delivery: FCA allows the goods to be handed over to the carrier at the seller's location or another location, whereas FOB requires the seller to load the goods onto the ship at the port of loading.
Transfer of Risk: In FCA, risk passes when the seller hands over the goods to the carrier, while in FOB, risk passes when the goods are loaded onto the ship.
Applicable modes of transportation: FCA can be applied to all modes of transportation (including land, sea, and air), while FOB is mainly applicable to sea freight.
Advantages of FCA
FCA incoterms offer greater flexibility and cost control benefits, as buyers and sellers are free to choose the most appropriate carrier and mode of transport according to their needs, and so the buyer can control the cost and the selection of routes well.
Limitations of FCA
Transfer of responsibility: Because the buyer is responsible for all the risks during transportation after the goods are handed over to the carrier, which may cause a certain burden for the buyer.
Information needs: The buyer needs to be fully aware of the carrier's capability and reputation to ensure the safe delivery of the goods to the destination.
Conclusion
FCA (Free Carrier) Incoterms provide a flexible and efficient transportation solution for international trade. Understanding how FCA Incoterms work, cost responsibilities, and comparison with other incoterms can help companies make more informed decisions in international transactions.
YQN Logistics encourages trade participants to be proactive in learning and adapting to these terms and looks forward to connecting with participants on a deeper level!